Outils pour utilisateurs
Panneau latéral
wiki:flossmanuals:ecologie-numerique:accueil
Table des matières
Écologie numérique - Modifier la résolution d'une image
Intention
Dans un principe d'écologie numérique, j'aimerai créer un variateur qui permet de transformer une image et de la compresser. L'idée est donc de diminuer la résolution d'une image en actionnant des potentiomètres. Pour l'instant j'ai réussis à diviser l'image en tableaux, l'idée étant ensuite de pouvoir éliminer certaines parties pour voir jusqu'où l'on peut dégrader l'image tout en la laissant visible.
Schéma de fonctionnement
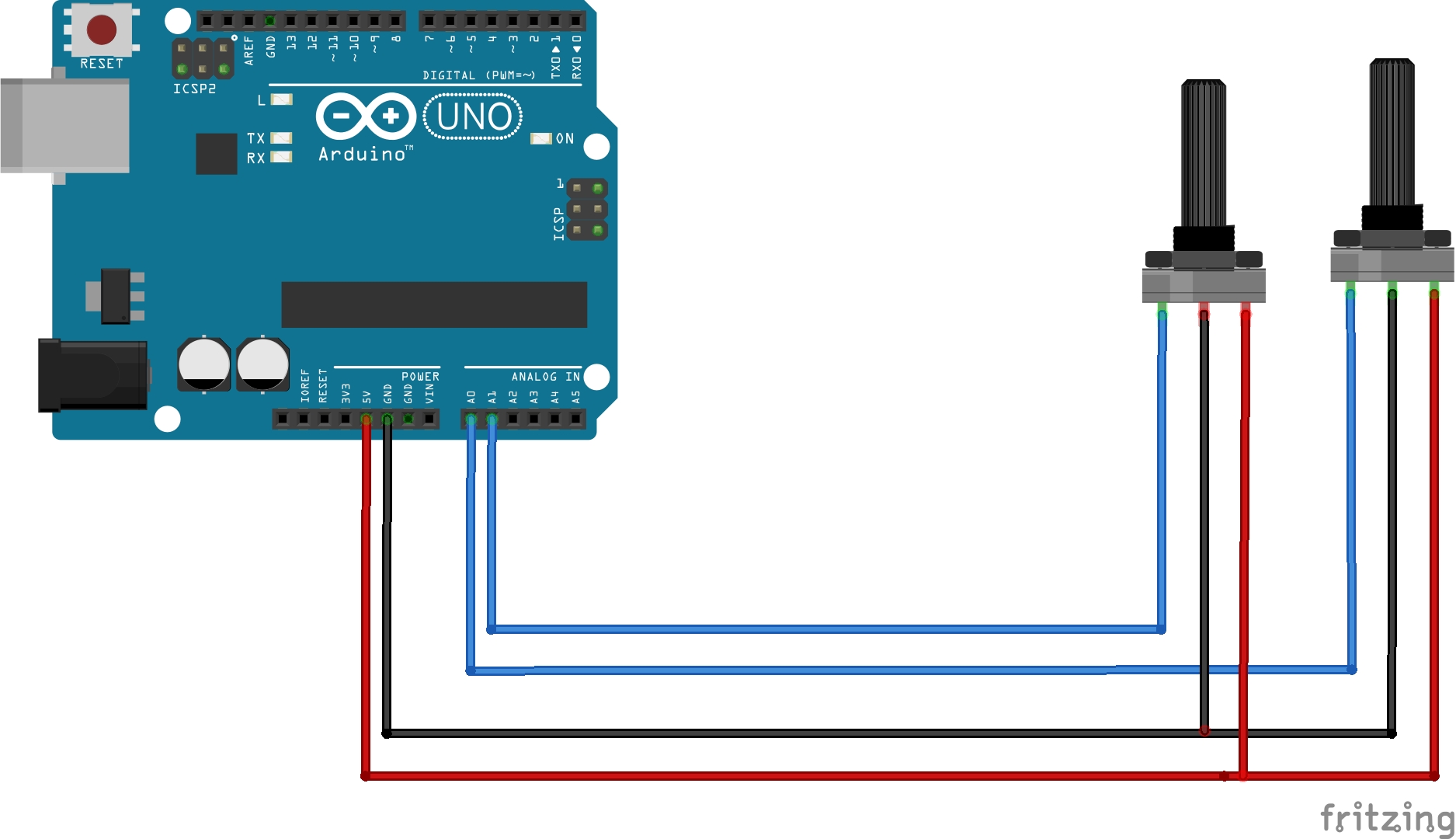
Schéma technique
Programme Arduino
int firstSensor = 0; // first analog sensor
int secondSensor = 0; // second analog sensor
int inByte = 0; // incoming serial byte
void setup() {
// start serial port at 9600 bps:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
establishContact(); // send a byte to establish contact until receiver responds
}
void loop() {
// if we get a valid byte, read analog ins:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// get incoming byte:
inByte = Serial.read();
// read first analog input, divide by 4 to make the range 0-255:
firstSensor = analogRead(A0) / 4;
// delay 10ms to let the ADC recover:
delay(10);
// read second analog input, divide by 4 to make the range 0-255:
secondSensor = analogRead(1) / 4;
// read switch, map it to 0 or 255L
// send sensor values:
Serial.write(firstSensor);
Serial.write(secondSensor);
}
}
void establishContact() {
while (Serial.available() <= 0) {
Serial.print('A'); // send a capital A
delay(300);
}
}
Programme Processing
import processing.serial.*;
PFont font;
PGraphics pg;
PImage img;
// communication ARduino
Serial myPort; // The serial port
int[] serialInArray = new int[3]; // Where we'll put what we receive
int serialCount = 0; // A count of how many bytes we receive
int x, y; // Starting position of the ball
boolean firstContact = false; // Whether we've heard from the microcontroller
void setup() {
size(800, 800, P2D);
img = loadImage("thibbckgpetite.jpg");
//font = createFont("ARIAL.TTF", 600);
pg = createGraphics(800, 800, P2D);
// paramètres de distorsion
x = width/2;
y = height/2;
// Print a list of the serial ports, for debugging purposes:
printArray(Serial.list());
// I know that the first port in the serial list on my mac
// is always my FTDI adaptor, so I open Serial.list()[0].
// On Windows machines, this generally opens COM1.
// Open whatever port is the one you're using.
String portName = Serial.list()[2];
myPort = new Serial(this, portName, 9600);
}
void draw() {
background(0);
// PGraphics
pg.beginDraw();
pg.background(0);
pg.fill(255);
//pg.textFont(font);
pg.textSize(800);
pg.pushMatrix();
pg.translate(width/2, height/2-215);
pg.textAlign(CENTER, CENTER);
pg.image(img, 0, 0);
pg.popMatrix();
pg.endDraw();
int tilesX = x+2;
int tilesY = y+2;
int tileW = int(width/tilesX);
int tileH = int(height/tilesY);
for (int y = 0; y < tilesY; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < tilesX; x++) {
// WARP
int wave = int(sin(frameCount * 0.05 + ( x * y ) * 0.07) * 20);
// SOURCE
int sx = x*tileW+ wave;
int sy = y*tileH;
int sw = tileW;
int sh = tileH;
// DESTINATION
int dx = x*tileW;
int dy = y*tileH;
int dw = tileW;
int dh = tileH;
copy(pg, sx, sy, sw, sh, dx, dy, dw, dh);
}
}
}
void serialEvent(Serial myPort) {
// read a byte from the serial port:
int inByte = myPort.read();
// if this is the first byte received, and it's an A,
// clear the serial buffer and note that you've
// had first contact from the microcontroller.
// Otherwise, add the incoming byte to the array:
if (firstContact == false) {
if (inByte == 'A') {
myPort.clear(); // clear the serial port buffer
firstContact = true; // you've had first contact from the microcontroller
myPort.write('A'); // ask for more
}
}
else {
// Add the latest byte from the serial port to array:
serialInArray[serialCount] = inByte;
serialCount++;
// If we have 2 bytes:
if (serialCount > 1 ) {
x = (int)map(serialInArray[0],0,255,0,width);
y = (int)map(serialInArray[1],0,255,0,height);
// print the values (for debugging purposes only):
println(x + "\t" + y );
// Send a capital A to request new sensor readings:
myPort.write('A');
// Reset serialCount:
serialCount = 0;
}
}
}
wiki/flossmanuals/ecologie-numerique/accueil.txt · Dernière modification: 2021/06/02 18:33 de damien.muti
Sauf mention contraire, le contenu de ce wiki est placé sous les termes de la licence suivante : CC Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International